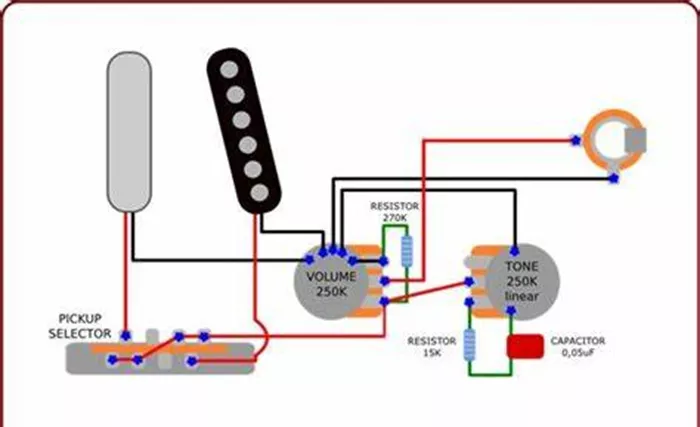
Guitar electronics form a delicate system where wire selection significantly impacts tone quality and instrument performance. As an electrical engineer with transformer expertise, I recognize how guitar wiring shares important principles with transformer design, particularly regarding signal integrity and electromagnetic interference. The wiring inside an electric guitar carries delicate audio signals from pickups to output jacks, much like transformer windings handle carefully balanced voltages in audio equipment.
Transformer technology relates to guitar wiring because both systems deal with low-voltage signals that require careful handling to prevent quality degradation. This relationship becomes particularly important when considering how proper wire selection affects signal transmission and noise rejection. While transformers efficiently transfer power between circuits, guitar wiring must preserve the nuanced characteristics of the instrument’s sound without adding interference or signal loss.
Essential Characteristics of Guitar Wiring
Wires used in guitar electronics must balance conductivity with flexibility while minimizing signal degradation. These requirements resemble those for transformer windings where conductor quality directly impacts performance. Most guitar wiring uses stranded copper conductors with various insulation types that provide physical protection while maintaining signal integrity.
The insulation system must prevent signal leakage while allowing for tight routing in confined guitar cavities. These electrical isolation requirements parallel those for transformer insulation where preventing unwanted coupling is critical. Proper wire selection prevents tone loss and maintains the instrument’s characteristic sound, similar to how transformer design preserves signal quality in audio applications.
Common Wire Types for Guitar Electronics
PVC Insulated Hook-Up Wire
PVC insulated wire represents the standard choice for most guitar wiring applications due to its excellent balance of performance and affordability. This wire type features multiple stranded copper conductors surrounded by durable PVC insulation that resists abrasion during installation. The construction allows for relatively easy routing through tight spaces while providing adequate protection against accidental shorts.
Available in various gauges from 22 AWG to 18 AWG, PVC insulated wire accommodates different wiring needs throughout the guitar. These size options parallel the conductor selections available for transformer connections in similar low-voltage applications. The color-coded insulation helps identify different circuit connections, much like color coding simplifies transformer wiring identification.
Shielded Audio Cable
For critical signal paths like pickup connections, shielded audio cable provides superior noise rejection. This cable type features a central conductor surrounded by a braided or spiral shield that grounds electromagnetic interference. The shielded construction resembles the protective measures used for transformer connections in sensitive audio equipment where noise rejection is paramount.
Shielded cable is commonly used for connections between pickups and controls in high-end guitars. These noise-sensitive requirements parallel those for transformer installations in recording equipment where clean signal transmission is essential. The cable’s robust design ensures minimal tone loss despite challenging electromagnetic environments.
Electrical Properties and Performance Factors
Capacitance and Tone Considerations
Proper wire selection must account for capacitance effects that can alter the guitar’s high-frequency response. These tonal considerations resemble the frequency response planning for audio transformers where conductor characteristics affect sound quality. Excessive capacitance can cause noticeable high-end loss, particularly in longer cable runs inside the guitar.
For optimal tone preservation, many guitar builders select low-capacitance wire specifically designed for audio applications. These specialized requirements parallel those for transformer-coupled audio circuits where signal integrity is critical. Careful wire selection prevents unwanted filtering of the instrument’s natural harmonics and overtones.
Current Carrying Requirements
While guitar signals involve minimal current, proper wire sizing still matters for maintaining signal strength. These current handling requirements parallel those for transformer secondary connections in low-power audio applications. Most guitar wiring uses 22 AWG to 18 AWG conductors that provide adequate current capacity without excessive bulk.
The wire must handle peak signal levels without introducing distortion or compression effects. These signal integrity requirements resemble those for transformer windings where clean signal transfer is essential. Proper conductor selection prevents signal degradation that could affect the instrument’s dynamic response and touch sensitivity.
Installation Methods and Best Practices
Soldering Techniques for Guitar Wiring
Proper soldering methods ensure reliable connections that withstand years of vibration and use. These installation requirements mirror those for transformer terminals where mechanical stability ensures long-term reliability. Modern guitar wiring practices include using high-quality solder and maintaining appropriate temperatures to prevent cold joints.
The NEC now requires neutral conductors at most switch locations to accommodate smart switches and future upgrades. These evolving requirements reflect how residential electrical systems must adapt to new technologies, similar to how transformer connections sometimes need modification for system upgrades. Proper stripping and termination methods prevent loose connections that could cause overheating or arcing faults.
Grounding and Shielding Methods
Effective grounding represents a critical element in guitar wiring to prevent hum and noise. These protective measures resemble the comprehensive grounding networks used with audio transformers that prevent unwanted interference. Modern guitar wiring typically includes a central ground point that connects all shielded components and cavities.
The grounding system must provide a low-impedance path for noise currents without creating ground loops. These noise rejection requirements parallel those for transformer installations in audio equipment where clean signal paths are essential. All metal components in the guitar should be properly grounded to maintain optimal shielding effectiveness.
Comparison with Alternative Wiring Methods
Solid Core vs Stranded Wire
Stranded conductors dominate guitar wiring due to superior flexibility and vibration resistance. These physical advantages parallel those of stranded transformer windings where mechanical durability is critical. While solid core wire may offer marginally lower resistance, its tendency to work harden and break makes it unsuitable for most guitar applications.
The flexible nature of stranded wire allows for easier routing through tight guitar cavities. This installation benefit resembles the space considerations in transformer design where compact windings improve performance. Proper conductor selection balances electrical performance with physical durability in the demanding guitar environment.
Teflon vs PVC Insulation
Teflon insulated wire offers higher temperature resistance and lower dielectric absorption than standard PVC. These material advantages parallel those of high-performance transformer insulation where signal purity is paramount. While more expensive, Teflon insulation may be justified in premium instruments where every aspect of tone matters.
The choice between insulation types depends on budget, installation requirements, and desired tonal characteristics. These decision factors resemble those considered when choosing between different transformer insulation materials where both performance and cost must be evaluated. Each approach has appropriate applications based on specific guitar design goals.
Future Developments in Guitar Wiring
Advanced Shielding Technologies
Modern guitars increasingly incorporate innovative shielding methods to combat electromagnetic interference. These evolving needs parallel the increasing sophistication of transformer shielding in sensitive audio equipment. Some manufacturers now use conductive paints or layered shielding foils to create comprehensive Faraday cages around electronics cavities.
Future guitar wiring may incorporate active shielding systems that adapt to changing electromagnetic environments. These advanced solutions resemble the adaptive technologies being developed for transformer installations in challenging RF environments. Proper shielding selection today should consider potential future upgrades to more advanced noise rejection systems.
Smart Guitar Integration
Emerging technologies are enabling guitars with integrated electronics and digital connectivity. These developments parallel the digital monitoring systems being incorporated into modern transformers. Some instruments now require additional conductors or communication cables to handle onboard processing and wireless transmission alongside traditional analog signals.
Future guitar wiring may incorporate hybrid analog/digital pathways that maintain vintage tone while adding modern capabilities. These integrated solutions resemble the combined power and data systems being developed for smart transformers. Proper wire selection today should anticipate potential future upgrades to more advanced guitar electronics systems.
Conclusion
Quality wiring forms the foundation of great-sounding guitar electronics, much like proper conductors ensure transformer performance. The relationship between wire selection and tone quality becomes particularly evident when considering how subtle electrical characteristics affect the instrument’s voice. Just as transformer design balances multiple engineering factors, guitar wiring must combine electrical performance with physical durability and tonal purity.
Ongoing developments in wiring technology continue to enhance guitar electronics while maintaining the instrument’s traditional character. These advancements parallel the innovations in transformer design where materials science and manufacturing improvements drive progress. By understanding wiring requirements and following best practices, guitar builders can create instruments that deliver exceptional tone and reliability.
The careful balance between conductor properties, insulation characteristics, and installation methods ensures guitar wiring will meet both current and future musical needs. This comprehensive approach mirrors the engineering considerations applied to transformer systems where multiple factors must be evaluated for optimal performance. Proper wire selection and installation ultimately determine the tonal quality, noise performance, and reliability of guitar electronics that musicians depend on.
Related Topics: